types of sinuses
Sphenoid Sinuses: The sphenoid sinuses are situated deep within the skull, behind the ethmoid sinuses and just above the nasopharynx. There is one sphenoid sinus on each side. These sinuses are less commonly involved in sinusitis but can contribute to headache symptoms when inflamed.
Nasal Septum: While not a sinus itself, the nasal septum is a partition that divides the nasal cavity into right and left sides. A deviated septum, where the septum is crooked or displaced to one side, can impact airflow through the nose and contribute to sinus issues.
Accessory Sinuses: In addition to the major paranasal sinuses, there are smaller, less well-defined sinuses referred to as accessory sinuses. These can include the frontal recess, agger nasi cells, and others. They can vary in size and location from person to person.
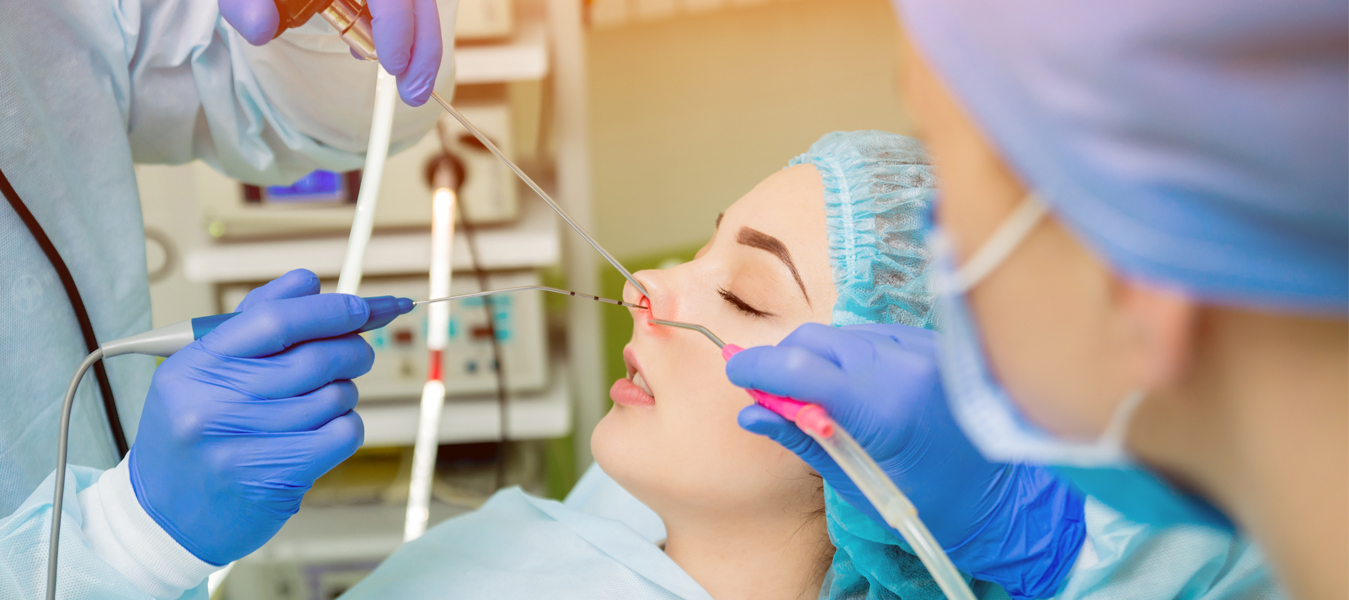
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Procedure
Removal of Tumors or Cysts (if needed): If there are tumors or cysts present in the sinuses, the surgeon will remove them during the surgery.
Irrigation and Cleaning: Saline solution is often used to irrigate the sinus cavities, helping to wash away debris, blood, and mucus.
Placement of Nasal Packing or Stents (if needed): In some cases, the surgeon may place nasal packing or stents to support the newly opened sinus passages and prevent them from closing too quickly.
Closure: Once the surgeon is satisfied with the results and has ensured proper drainage and ventilation, the endoscope is removed, and the surgical site is carefully closed.
Recovery: You will be closely monitored as you wake up from anesthesia. In most cases, patients can return home on the same day or the following day.
Precautions of Sinus Surgery
Diet: Maintain a balanced diet to support healing. Ensure you stay hydrated and consume foods rich in vitamins and nutrients. Avoid spicy or hot foods that may irritate the nasal passages.
Avoid Irritants: Stay away from environments or substances that could irritate the nasal passages, such as dust, smoke, strong odors, and allergens.
Protection from Infection: Minimize the risk of infection by practicing good hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with individuals who have colds or contagious illnesses.
Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. These appointments are essential for monitoring your progress, removing any packing or splints, and addressing any concerns.
Returning to Activities: Gradually resume normal activities only when cleared by your surgeon. Avoid activities that could put stress on the surgical area until you receive approval.
Be Patient: Understand that recovery times can vary. Be patient with the healing process, and do not rush back into your regular routine until your surgeon advises it.
Monitor for Complications: Keep an eye on the surgical site for signs of complications, such as excessive bleeding, severe pain, increasing swelling, or signs of infection. If you experience any concerning symptoms, contact your surgeon promptly.
Risk Factor
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Leak: In rare cases, sinus surgery can result in a CSF leak, where fluid that surrounds the brain leaks into the nasal cavity. Symptoms may include clear nasal discharge, headaches, or salty taste in the throat. A CSF leak requires prompt medical attention.
Eye Complications: The proximity of the eyes to the sinuses can lead to eye-related complications, such as swelling, bruising, or visual changes in rare instances.
Nasal Septal Perforation: Perforation or a hole in the nasal septum (the thin wall separating the nasal passages) can occur as a complication of sinus surgery. This may affect nasal airflow and require further treatment.
Anesthesia Risks: Like any surgery, there are inherent risks associated with anesthesia, including allergic reactions and complications. Anesthesia is administered and monitored by trained professionals to minimize these risks.
Unsatisfactory Results: There is a possibility that sinus surgery may not fully alleviate the symptoms or conditions for which it was performed. Some individuals may require additional procedures or treatments.
