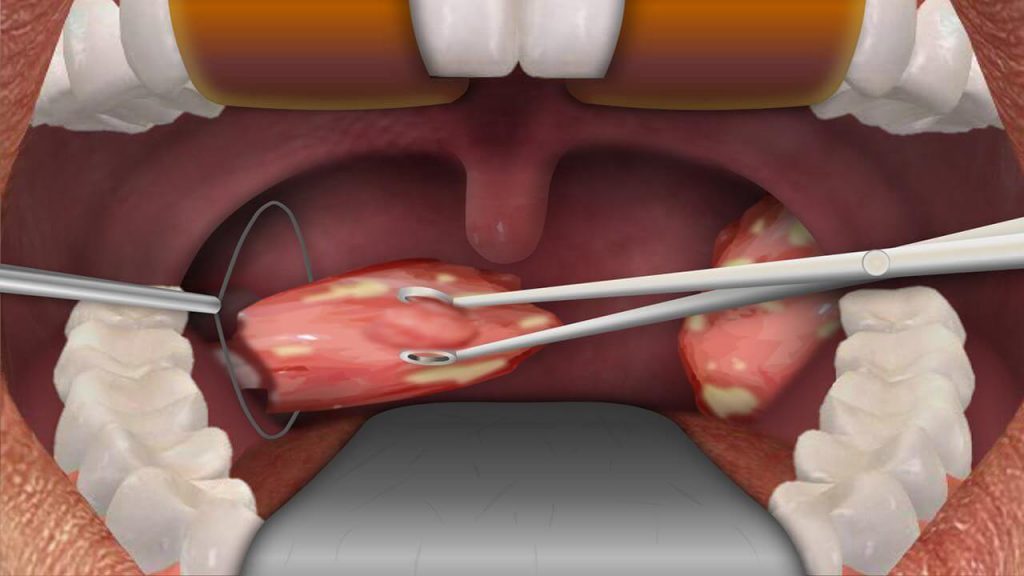
Types of Tonsil Surgery
Cold Knife (Steel Scalpel) Tonsillectomy: In this traditional method, the surgeon uses a steel scalpel to dissect and remove the tonsils. Thus This technique has been use for many years and is still considere effective.
Electrocautery Tonsillectomy: Electrocautery involves the use of an electrically heate instrument to cut and cauterize (seal) blood vessels during surgery. For instance, It can help minimize bleeding during the procedure.
Coblation Tonsillectomy: Coblation is a relatively newer technique that uses radiofrequency energy to break down. Thus, remove the tonsil tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Once, This method is known for its reduced pain and faster recovery compared to traditional methods.
Laser Tonsillectomy: Laser tonsillectomy utilizes a laser beam to vaporize or remove the tonsil tissue. Once, It can be use to target specific areas, making it a precise method. Laser tonsillectomy may be preferre for certain cases.
Ultrasonic Tonsillectomy: Ultrasonic energy is use to break down and remove tonsil tissue in this method. It can be considered for some patients, although .thus, it’s not as commonly use as other techniques.
Common symptoms of tonsillitis
Sore Throat: A sore throat is one of the hallmark symptoms of tonsillitis. It can be quite painful and may make swallowing difficult.
Swollen Tonsils: The tonsils themselves may appear red, swollen, and enlarge. In some cases, they can become covere in a white or yellowish coating or patches.
Painful or Difficulty Swallowing: Due to the sore throat and swollen tonsils, it can be painful or uncomfortable to swallow food and liquids.
Fever: Tonsillitis can cause a fever, especially in cases of bacterial tonsillitis. The fever may be mild to high-grade.
Headache: Some people with tonsillitis experience headaches, which can be associate with the general discomfort and fever.
Ear Pain: Tonsillitis can sometimes cause referre pain to the ears, leading to earaches.
Treatment Options Common Tonsil problems
Tonsillitis (Bacterial or Viral Infections):
- Viral Tonsillitis: Most cases of viral tonsillitis are manage with supportive care.Similarly, This includes rest, staying hydrate, .thus, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen .for instnace, ibuprofen to alleviate pain and fever.visit our Hospital!
- Bacterial Tonsillitis (Strep Throat): Firstly, Bacterial tonsillitis, often cause by Streptococcus bacteria.Once is typically treate with antibiotics prescribe by a healthcare provider. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics.thus, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Recurrent Tonsillitis:
- If someone experiences frequent and severe bouts of tonsillitis, a healthcare provider may consider a tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) as a treatment option.
Enlarged Tonsils:
- Enlarge tonsils that do not cause significant health problems may not require treatment.
- If enlarge tonsils are obstructing the airway, causing sleep apnea, or affecting swallowing, treatment options may include:
- Observation and monitoring for mild cases.
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime for sleep apnea.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy for sleep apnea.
- Tonsillectomy if the condition is severe or not responsive to other treatments.
Tonsil Stones (Tonsilloliths):
- Small tonsil stones may not require treatment.
- Gargling with warm salt water and maintaining good oral hygiene can help prevent tonsil stones.
- In cases of persistent discomfort or larger tonsil stones, a healthcare provider or ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist may manually remove them or recommend a tonsillectomy if they are causing chronic issues.
Chronic Tonsillitis or Tonsillar Abscess:
- Chronic tonsillitis that does not respond well to antibiotics or recurring tonsillar abscesses may necessitate a tonsillectomy as a treatment option.
Risks and Complications
Tonsillitis (Bacterial or Viral Infections):
- Viral Tonsillitis: Most cases of viral tonsillitis are managed with supportive care. This includes rest, staying hydrated, and over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to alleviate pain and fever.
- Bacterial Tonsillitis (Strep Throat): Bacterial tonsillitis, often caused by Streptococcus bacteria, is typically treated with antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Recurrent Tonsillitis:
- If someone experiences frequent and severe bouts of tonsillitis, a healthcare provider may consider a tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) as a treatment option.
Enlarged Tonsils:
- Enlarged tonsils that do not cause significant health problems may not require treatment.
- If enlarged tonsils are obstructing the airway, causing sleep apnea, or affecting swallowing, treatment options may include:
- Observation and monitoring for mild cases.
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime for sleep apnea.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy for sleep apnea.
- Tonsillectomy if the condition is severe or not responsive to other treatments.
Tonsil Stones (Tonsilloliths):
- Small tonsil stones may not require treatment.
- Gargling with warm salt water and maintaining good oral hygiene can help prevent tonsil stones.
- In cases of persistent discomfort or larger tonsil stones, a healthcare provider or ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist may manually remove them or recommend a tonsillectomy if they are causing chronic issues.
Chronic Tonsillitis or Tonsillar Abscess:
- Chronic tonsillitis that does not respond well to antibiotics or recurring tonsillar abscesses may necessitate a tonsillectomy as a treatment option.
